What is AWS in Simple Words?
Discover AWS in simple terms at GalaxyonKnowledge. Learn how Amazon Web Services revolutionizes cloud computing and enhances business efficiency.
Understanding What AWS Is in Simple Words
In today’s digital world, cloud computing has become an essential part of how businesses and individuals operate online. Among the many cloud service providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out as a leading platform that offers a wide array of cloud-based solutions. But for those unfamiliar with the technical jargon, understanding what AWS really is can seem overwhelming. This article aims to explain What AWS is in simple words, breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand language while highlighting its importance and core functionalities.
What is AWS? An Introduction to Cloud Computing
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a comprehensive cloud computing platform provided by Amazon. It allows users to access a vast network of remote servers hosted across the globe to store data, run applications, and manage IT infrastructure without having to own physical hardware. Simply put, AWS provides the tools and services needed to operate websites, applications, or even entire data centers via the internet. It’s like renting computing power and storage instead of buying and maintaining physical servers yourself.
AWS's primary goal is to make technology more accessible, flexible, and scalable for everyone—from small startups to large corporations. Instead of investing heavily in infrastructure that may become obsolete quickly, users can leverage AWS’s on-demand resources that adapt to their needs. This approach not only reduces costs but also accelerates innovation by allowing rapid deployment of new ideas. Overall, AWS simplifies complex IT processes into manageable cloud services that anyone can use with minimal technical expertise.
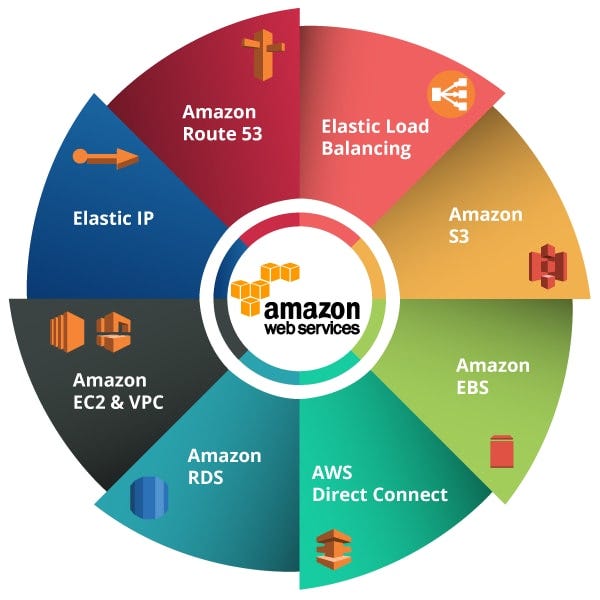
The Core Components of AWS: Understanding Its Building Blocks
AWS encompasses a broad spectrum of services designed to meet various technological needs. These core components serve as the foundation for building and managing applications efficiently within the cloud environment. Understanding these components helps demystify what AWS offers in simple terms.
At its heart, AWS provides compute resources such as virtual servers called EC2 instances that enable users to run applications just like they would on physical machines. Storage options like S3 (Simple Storage Service) allow users to store any amount of data securely in the cloud and access it from anywhere at any time. Databases are also available through managed services such as RDS (Relational Database Service), which simplifies database management tasks.
Additional key components include networking services like VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), which creates isolated networks within AWS for enhanced security; security tools such as IAM (Identity and Access Management), ensuring only authorized users can access specific resources; and monitoring services like CloudWatch that help track system performance. These foundational elements work together seamlessly so businesses can focus on developing their applications rather than managing infrastructure.
Amazon EC2: Virtual servers tailored for scalable computing power.
Amazon S3: Reliable storage for files, images, videos, and backups.
Amazon RDS: Managed database service simplifying database setup.
VPC: Isolated network environments within AWS for security.
IAM: User access control ensuring security compliance.
CloudWatch: Monitoring tools providing insights into system health.
By combining these core components, organizations gain a flexible environment capable of supporting diverse workloads—ranging from simple websites to complex machine learning projects—all without significant upfront investments.
How Does AWS Work? The Mechanisms Behind Its Functionality
Understanding how AWS operates helps clarify its role as a cloud service provider that empowers users globally. At its core, AWS functions through a network of data centers strategically located around the world—these are often called regions or availability zones—and provide on-demand access to computing resources.
When you sign up for an AWS account, you can choose where your resources will be hosted based on your geographical preferences or latency requirements. You then deploy virtual servers (EC2 instances), store data in S3 buckets, or set up databases—all through user-friendly dashboards or APIs. These resources are billed based on usage; if you need more capacity during peak times, you simply scale up effortlessly. Conversely, when demand decreases, you can reduce your resource consumption without penalty.
AWS employs virtualization technology to partition physical hardware into multiple virtual environments — enabling multiple users to share server capacity securely and efficiently. This multi-tenancy model ensures optimal utilization while maintaining strict isolation between different customers’ workloads. Additionally, advanced security protocols protect data integrity during transmission and storage.
The seamless scalability offered by AWS means that businesses do not need to predict their future infrastructure needs precisely; they can adapt quickly as their operations grow or change. This flexible operation model makes it easier for companies to innovate without worrying about hardware limitations or costly upgrades.
On-demand provisioning: Resources are available whenever needed without prior planning.
Pay-as-you-go billing: Costs directly correlate with actual usage.
Virtualization technology: Physical hardware is divided into multiple secure virtual environments.
Global infrastructure: Data centers across various regions ensure low latency and high availability.
Scalability: Resources can be expanded or contracted instantly based on business needs.
In essence, AWS acts as an intelligent intermediary between users and physical infrastructure—making complex hardware management obsolete while providing powerful computing capabilities at your fingertips.
Benefits of Using AWS: Why Businesses Choose Cloud Over Traditional Infrastructure
Choosing cloud services like AWS offers numerous advantages over traditional on-premises IT setups. These benefits are fundamental reasons why many organizations transition their operations into the cloud environment provided by AWS.
One significant benefit is cost savings; instead of investing heavily in purchasing servers and maintaining them constantly—costs associated with electricity, cooling, staffing—businesses pay only for what they use through flexible pricing models. This shift reduces capital expenditure (CapEx) into operational expenses (OpEx), making IT spending more predictable and manageable.
Another advantage is agility—the ability to deploy new applications rapidly without waiting weeks or months for hardware procurement or setup. With just a few clicks or API commands, teams can launch new environments instantly—a critical feature in today’s fast-paced market landscape. Furthermore, scalability allows businesses to handle sudden spikes in demand seamlessly without risking downtime or performance issues.
Security features built into AWS provide peace of mind: data encryption both at rest and during transmission protects sensitive information; identity management systems restrict access appropriately; compliance standards ensure regulatory requirements are met across industries like healthcare or finance. Additionally, disaster recovery solutions within AWS enable quick backup restoration if something goes wrong—minimizing potential downtime risks significantly.
Other notable benefits include:
Flexibility in choosing operating systems and software configurations
Automatic updates reduce maintenance efforts
Collaboration opportunities across geographically dispersed teams
Environmental sustainability due to energy-efficient data centers
Overall, leveraging AWS empowers organizations with modern technological advantages that foster innovation while reducing operational burdens—a compelling reason many enterprises prefer this cloud platform over traditional infrastructure models.
Security Measures in Place: How Does AWS Protect Your Data?
Security remains one of the most crucial concerns when adopting any cloud service platform like AWS. As such, understanding how AWS safeguards user data helps build trust and confidence in utilizing its services effectively.
AWS employs multiple layers of security measures designed to protect both data at rest (stored data) and data during transit (being transmitted). It uses advanced encryption protocols that prevent unauthorized access during storage or communication phases. Additionally, strict access controls via Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies ensure only authorized personnel have permissions aligned with their roles—limiting potential breaches from insider threats or external attacks.
Physical security forms another vital aspect; all data centers are equipped with comprehensive surveillance systems alongside biometric controls requiring authorized personnel verification before entry occurs—ensuring robust protection against physical intrusion attempts. Network security features include firewalls configured specifically for each customer environment along with intrusion detection systems monitoring unusual activity patterns continuously.
Furthermore, compliance certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3 attestations demonstrate that Amazon adheres to globally recognized standards concerning information security management systems (ISMS). Regular audits ensure ongoing adherence while helping identify vulnerabilities proactively before they become serious threats.
AWS also provides tools enabling customers themselves to enhance their security posture—for instance:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of verification when accessing sensitive resources.
Data encryption keys management through Key Management Service (KMS)
Automated vulnerability scanning mechanisms
Security best practices documentation tailored for different industries
Ultimately, by implementing comprehensive security measures ranging from physical safeguards at data centers worldwide down to software-level protections within user accounts—and empowering clients with control options—AWS ensures your valuable data remains protected against evolving cyber threats at all times.
How Can You Use AWS? Practical Steps for Beginners
Getting started with AWS might seem daunting initially due to its extensive range of services; however, the process becomes straightforward once you understand basic steps involved in deploying resources within this cloud platform.
First step involves creating an account on the official Amazon Web Services website—you’ll need an email address and credit card details since billing occurs based on usage. Next comes familiarizing yourself with the dashboard interface known as the Management Console—it provides visual tools for managing all aspects of your cloud environment easily without deep technical skills initially required.
Once logged in successfully:
Decide what kind of resource you want: e.g., hosting a website using EC2 instances.
Launch your first virtual server by selecting pre-configured templates suited for common applications.
Configure necessary settings such as region location depending on your target audience.
Upload content or install software onto your server via remote desktop connections.
Set up storage solutions like S3 buckets if storing media files or backups are necessary.
Implement security measures including setting permissions through IAM roles.
Monitor performance regularly using CloudWatch dashboards so you can optimize resource utilization accordingly.
Many tutorials available online guide step-by-step procedures tailored toward beginners aiming at deploying simple projects initially before scaling up complexity gradually over time—all these practical steps help demystify how everyday users leverage powerful capabilities within just minutes after signing up!
By following these straightforward procedures along with continuous learning about additional features offered by AWS—such as serverless computing with Lambda functions—you’ll find yourself increasingly comfortable navigating this versatile cloud ecosystem capable of supporting virtually any digital project you envision today or tomorrow.
The Future of Cloud Computing With AWS
As technology continues evolving rapidly worldwide, so does the role of platforms like AWS shaping our digital future significantly more than ever before—a trend driven by increasing reliance on automation, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics—and much more innovative applications yet unseen today.
AWS invests heavily in research & development initiatives aimed at expanding capabilities further — integrating quantum computing prototypes; enhancing machine learning frameworks; developing edge computing devices closer geographically to end-users—to reduce latency dramatically; fostering hybrid-cloud environments combining private on-premises hardware seamlessly integrated with public clouds; supporting IoT ecosystems connecting billions devices reliably across industries such as manufacturing automation or smart cities initiatives—all underpinned by scalable secure architectures designed explicitly for future challenges ahead.
This continuous innovation promises increased efficiency gains coupled with smarter workflows reducing manual intervention drastically across sectors—from healthcare diagnostics powered by AI algorithms analyzing vast datasets—to financial institutions employing blockchain technologies facilitating transparent transactions globally—all contributing towards shaping an interconnected digital universe where businesses thrive thanks largely due to flexible trustworthy infrastructures offered freely via platforms like Amazon Web Services today—and surely well into tomorrow’s technological horizon too.
A Clearer Picture: What Is AWS in Simple Words?
In essence, Amazon Web Services represents a revolutionary shift from traditional IT methods toward flexible cloud-based solutions accessible anytime anywhere over the internet—a platform offering scalable compute power combined with reliable storage options backed by enterprise-grade security measures—all designed to empower businesses regardless of size or industry background while reducing costs significantly along the way.Today's organizations increasingly rely on this dynamic ecosystem not merely because it simplifies complex processes but because it unlocks unprecedented potential for growth innovation—making "what is AWS" not just about technology but about transforming how we think about digital possibilities forevermore.